Hormonal Hair Growth
Our bodies are remarkable, intricate systems, regulated by a delicate balance of hormones that help to maintain homeostasis and overall well-being in the human body. However, disruptions in this hormonal equilibrium can lead to a number of various (and incredibly common) health conditions. One such manifestation of hormonal imbalance is none other than excessive hair growth, which can be both a cosmetic concern and a symptom of an underlying hormonal disorder. While there is no need to feel ashamed of excessive hair growth, it is important to acknowledge its potential impact on an individual’s self-esteem. Therefore, gaining a deeper understanding of the mechanisms through which hormones contribute to this condition can be valuable in determining the most effective treatment approaches.
In this blog, we will explore some common hormonal conditions that cause excess hair growth, shedding light on their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. If you’re ready to win the war against unwanted hair growth, simply read on to find out more.
1. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a common endocrine disorder affecting 8-13% of women of reproductive age. In fact, chances are you probably know someone who suffers from PCOS. This condition is characterised by hormonal imbalances, resulting in irregular menstruation, ovarian cysts, and excessive hair growth (hirsutism). While the exact cause of the hormonal imbalance in PCOS is not fully understood, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Generally, elevated levels of androgens, such as testosterone, are responsible for the many symptoms observed in PCOS patients. Additionally, PCOS can also lead to other complications like insulin resistance, weight gain, and fertility issues. Typically, diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, hormone level tests, and pelvic ultrasound.
It is important to note that not all women with PCOS will experience excessive hair growth, and the severity can vary among individuals. However, for those affected, managing the hormonal imbalance through lifestyle changes, medications, and specific laser hair removal techniques can help reduce unwanted hair growth and improve self-esteem.
2. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia is a genetic disorder that affects the adrenal glands, responsible for producing essential hormones like cortisol and aldosterone. The most common form of CAH, known as 21-hydroxylase deficiency, leads to decreased cortisol production and increased androgen levels. Excessive androgens can result in virilisation in females, including excessive hair growth in areas where it is typically minimal or absent in, such as the face, chest, back, and limbs. It’s important to note that CAH is a complex condition with different forms and varying degrees of androgen excess.
When it comes to managing excessive hair growth caused by CAH, there are several options available for hair removal, including shaving, waxing, depilatory creams or laser hair removal that provides longer-lasting results. However, it is important to remember that while hair removal methods can help manage excessive hair growth, addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance associated with CAH through appropriate medical management is essential for long-term control of symptoms.
3. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism refers to an overactive thyroid gland, which produces an excess of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). While hair loss is a well-known symptom of thyroid disorders, some individuals with hyperthyroidism may experience paradoxical excessive hair growth. For example, some individuals with underlying hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or adrenal disorders, may experience both hyperthyroidism and excessive hair growth simultaneously. In such cases, the excessive hair growth is more likely related to the underlying hormonal disorder rather than hyperthyroidism itself.
Either way, if you are experiencing unusual hair growth alongside hyperthyroidism or have concerns about your hair growth patterns, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your specific situation and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to assess thyroid hormone levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. Treatment options may include medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery, depending on the underlying cause and severity.
4. Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s Syndrome occurs when the body is exposed to high levels of the hormone cortisol for an extended period. Cortisol belongs to a group of hormones called glucocorticoids, which have various effects on different tissues and organs, including the hair follicles. This condition can be caused by prolonged use of corticosteroid medications or an overactive adrenal gland. Cortisol interacts with androgen receptors present in the hair follicles, leading to an increased sensitivity to androgens (male hormones) or mimicking their effects. Androgens, such as testosterone, can promote the growth of terminal (thick, coarse) hair in areas where it is typically minimal or absent in females. Additionally, cortisol can influence the balance of other hormones, such as oestrogen and progesterone, which play a role in hair growth regulation. The disruption of this hormonal balance can contribute to changes in hair growth patterns.
5. Post-Menopause
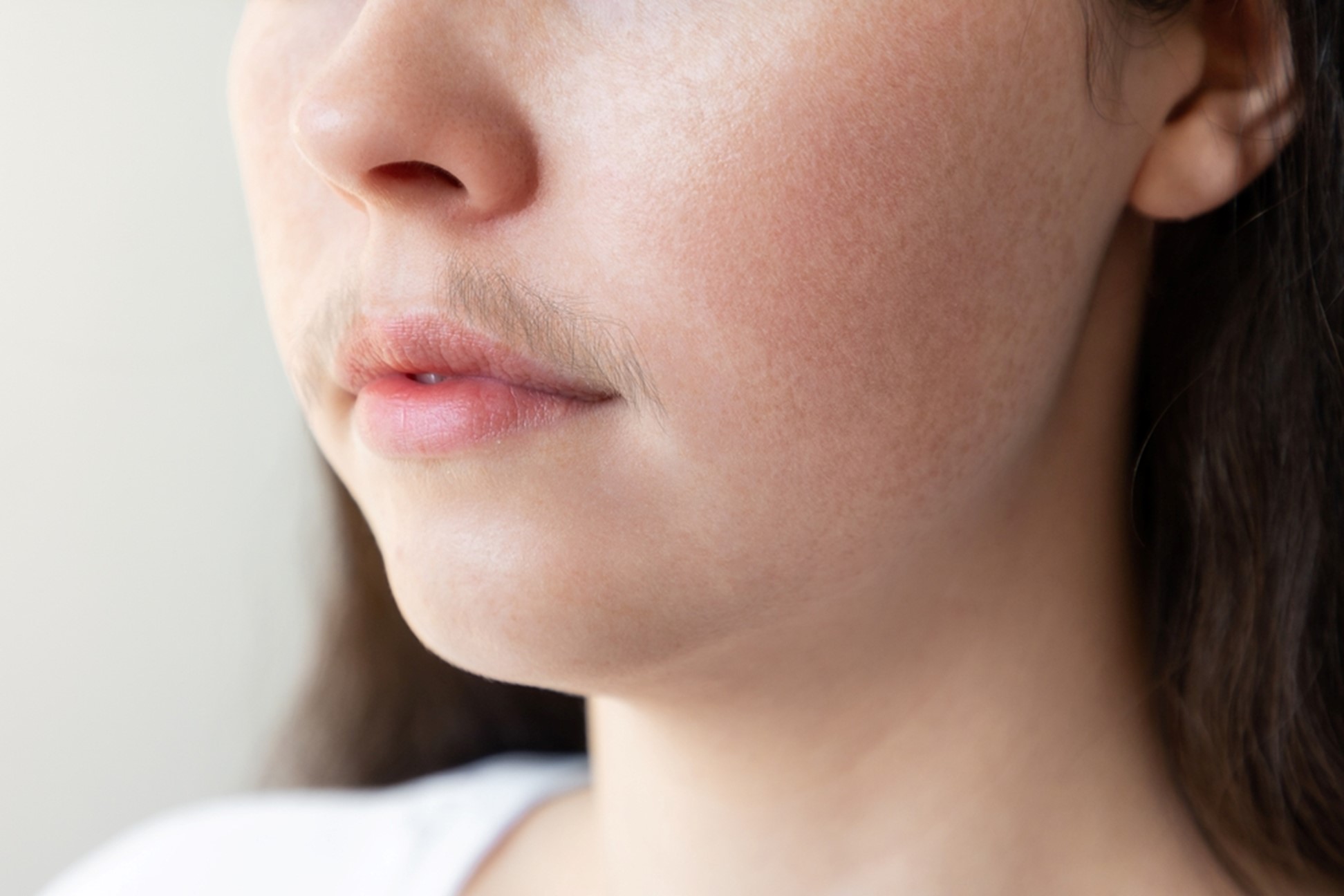
During menopause, a woman’s oestrogen levels decline significantly, while androgen levels (such as testosterone) remain relatively stable or may even slightly increase due to a decrease in oestrogen’s inhibitory effect on androgen production. These hormonal shifts in the body can often contribute to the growth of excess facial hair, which may manifest as the development of a moustache or whiskers. However, it is important to note that the exact cause of excessive hair growth during menopause can vary among individuals. Factors such as genetics, ethnicity, and underlying hormonal imbalances may contribute to the development of excessive facial hair. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as the above-mentioned polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can be associated with excessive hair growth and may coincide with menopause.
How We Can Help
While excessive hair growth is incredibly common and should not warrant shame, it can undeniably affect an individual’s self-esteem. If you are looking to counter the effects of hormonal hair growth, we are here to help. At Medical Aesthetic, our teams expertise is in treating hormonal-related hair growth, providing safe and effective solutions such as laser hair removal to help you achieve your hair and skin care goals. Regardless of the hormonal condition you’re experiencing, we provide customised solutions to address and eliminate your concerns with hair growth. More importantly, our mission is to empower our clients with the knowledge and tailor made solutions to deliver long term results without breaking the bank.
Contact us today to book your consultation today and discover the freedom of smooth, hair-free skin.